
Can we rely on the best trial? A comparison of individual trials and systematic reviews. Misuse of ‘trend’ to describe ‘almost significant’ differences in anaesthesia research.
#SYSTEMATIC REVIEW VS META ANALYSIS DIFFERENCE HOW TO#
When and how to update systematic reviews: consensus and checklist. Investigating clinical heterogeneity in systematic reviews: a methodologic review of guidance in the literature. Gagnier JJ, Moher D, Boon H, Beyene J, Bombardier C. Uncertainty in Heterogeneity Estimates in Meta-Analyses. 2017 6:S412–3.Įvangelou E, Ioanidis JPA, Patsopoulos NA. The problem of mixing ‘apples and oranges’ in meta-analytic studies. Meta-analysis: principles and procedures. The use of numbers needed to treat derived from systematic reviews and meta-analysis: caveats and pitfalls. The existence of publication bias and risk factors for its occurrence. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.0 (updated July 2019). In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Chapter 10: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses of randomised trials: principles and pitfalls. Confidence intervals permit, but do not guarantee, better inference than statistical significance testing. 2018 18:85.Ĭoulson M, Healey M, Fidler F, Cumming G. Defining the process to literature searching in systematic reviews: a literature review of guidance and supporting studies. 2005 2:260–4.Ĭooper C, Booth A, Varley-Campbell J, Britten N, Garside R. The use of systematic reviews when designing studies. Clinical trials should begin and end with systematic reviews of relevant evidence: 12 years and waiting. Applicable or non-applicable: investigations of clinical heterogeneity in systematic reviews. Conducting systematic evidence reviews: core concepts and lessons learned. 2017,6: Article 245.īrown PA, Harniss MK, Schomer KG, Feinberg M, Cullen NK, Johnson KL. Optimal database combinations for literature searches in systematic reviews: a prospective exploratory study. 2011 11:41.īramer WM, Rethlefsen ML, Kleijnen J, Franco OH. Quantifying, displaying and accounting for heterogeneity in the meta-analysis of RCTs using standard and generalised Q statistics. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. 2008 61:857–65.īorenstein M, Hedges LV, Higggins JPT, Rothstein HR. Attention should be given to multiplicity issues in systematic reviews. īender R, Bunce C, Clarke M, Gates S, Lange S, Pace NL, Thorlund K. Seventy-five trials and eleven systematic reviews a day: How will we ever keep up? PLoS Med. 2018 7:195.īastian H, Glasziou P, Chalmers I. Time-to-update of systematic reviews relative to the availability of new evidence. Odds ratio vs risk ratio in randomised controlled trials. 2008 11:121–31.īalasubramanian H, Ananthan A, Rao S, Patole S. A new approach to outliers in meta-analysis. This chapter focuses on the critical appraisal of a systematic review and meta-analysis based on their principles and practice. Without transparency about what was done, and how it was done, it is difficult to reproduce the results, questioning the validity of any study. Reproducibility is a critical aspect of science. However, the methodological rigour (design, conduct, analysis, interpretation, and reporting) of both, the systematic review and meta-analysis and the included studies deserve equal attention for judging the validity of the findings of a systematic review. Given the hierarchy of evidence-based medicine, a systematic review and meta-analysis are expected to provide robust evidence to guide clinical practice and research. A systematic review may or may not contain a meta-analysis for various reasons.
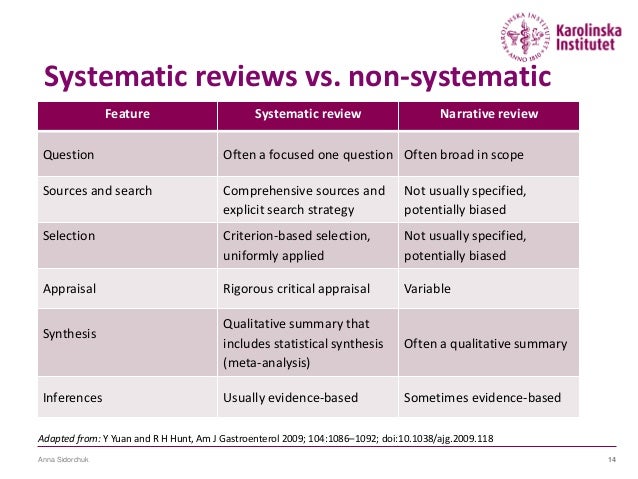


They focus on a specific question and use clearly stated, prespecified scientific methods to identify, select, assess, and summarise the findings of similar but separate studies. Systematic reviews are the most reliable and comprehensive statement about what works.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
